Examples
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
To get started, we essentially need two things:
A graph construction method (see Graph construction)
A construction method for the conditionals (see Conditionals)
from bn_testing.models import BayesianNetwork
from bn_testing.dags import ErdosReny
from bn_testing.conditionals import PolynomialConditional
model = BayesianNetwork(
n_nodes=20,
dag=ErdosReny(p=0.1),
conditionals=PolynomialConditional(max_terms=2),
random_state=20)
model.show()
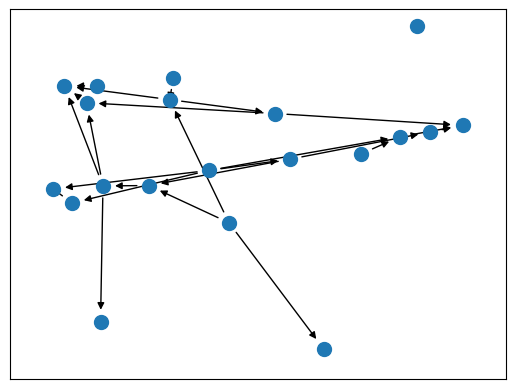
After the model has been generated, all transformations have been
stored in model.transformations:
{
'f00': 8.1*f01^5 + -9.7*f01^5,
'f01': -8.9*f10^5 + -1.6*f10^5,
'f02': 4.6*f19^5 + 3.8*f19^5,
'f03': -9.9*f05^2 + -8.6*f05^2,
'f05': -9.4*f12^7 + 3.2*f12^7,
'f06': -3.8*f05^6*f02^2,
'f08': -7.1*f10^2*f04^1 + -9.4*f10^1*f04^2,
'f09': -7.2*f19^2*f05^1*f07^1*f06^1 + 3.7*f19^1*f05^2*f07^1*f06^1
'f12': 6.5*f16^3*f01^1 + 6.2*f16^1*f01^3,
'f13': 6.7*f16^4,
'f15': 9.6*f08^1*f00^7*f02^4,
'f17': -5.5*f10^6,
'f18': -9.3*f10^4*f17^2,
'f19': -2.7*f16^7*f14^4,
}
Sampling
df = model.sample(10000)
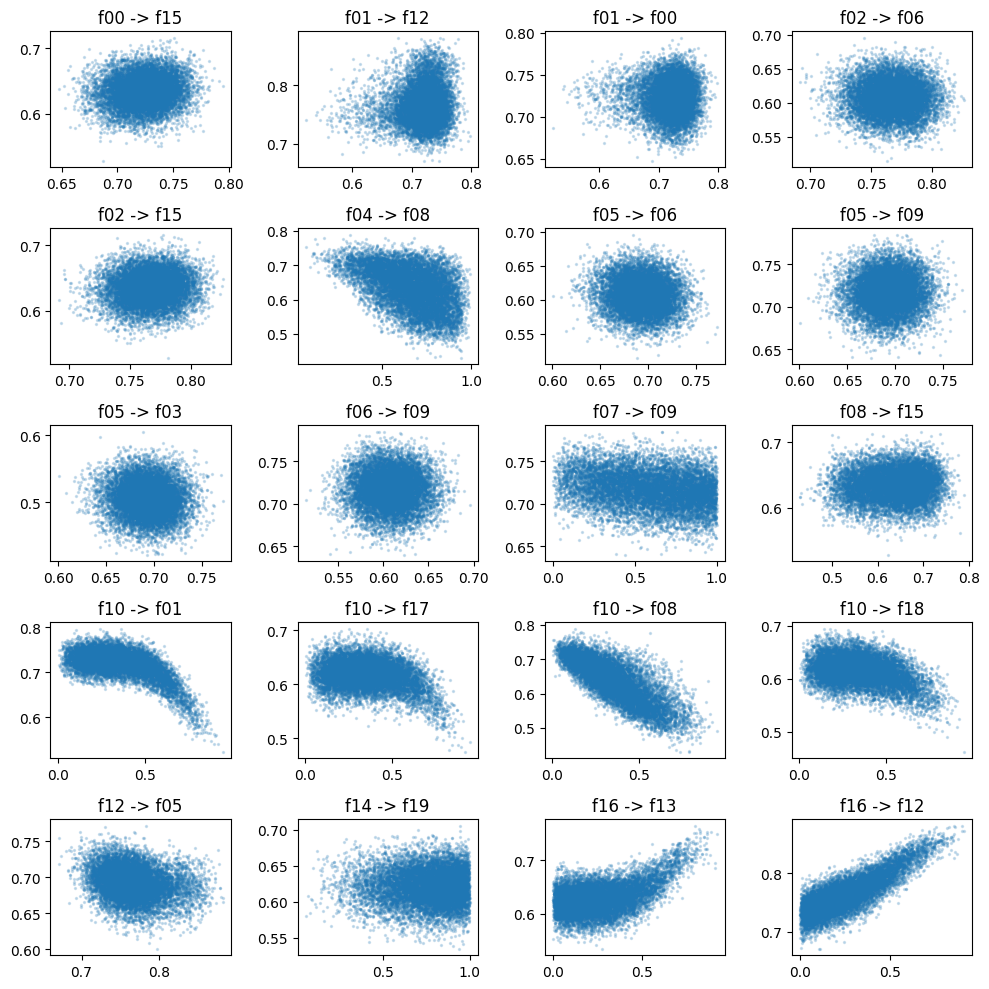
Edge scatters
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10), ncols=4, nrows=5)
for edge, ax in zip(model.edges, axes.ravel()):
ax.scatter(df[edge[0]], df[edge[1]], alpha=0.2, s=2)
ax.set_title(f"{edge[0]} -> {edge[1]}")
fig.tight_layout()
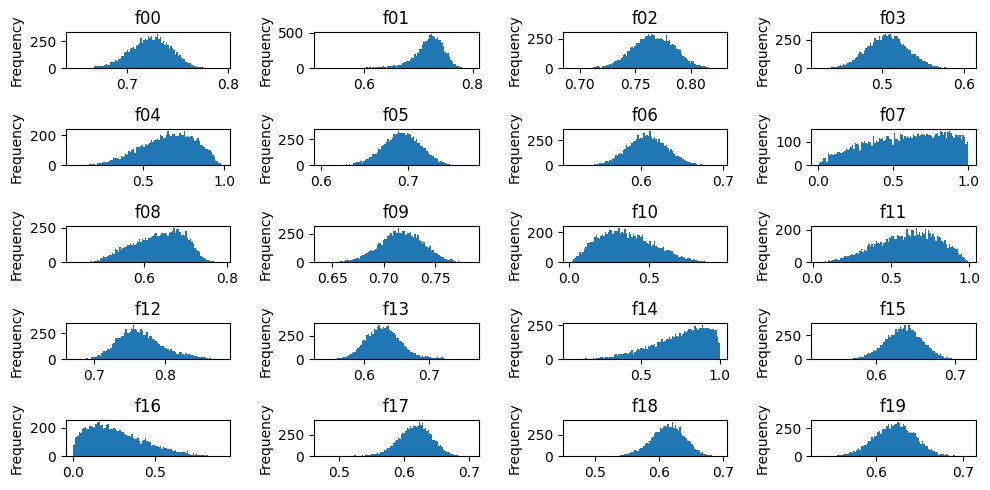
Marginal distributions
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5), ncols=4, nrows=5)
for ax, c in zip(axes.ravel(), df.columns):
df[c].plot.hist(ax=ax, bins=100)
ax.set_title(c)
fig.tight_layout()
Saving and loading
A model object can be saved to disk as follows:
model.save('/path/to/model.pkl')
Afterwards, it can be loaded using:
from bn_testing.models import BayesianNetwork
model = BayesianNetwork.load('/path/to/model.pkl')